Why ?
- Legal requirement in most countries
- Moral responsibility to employees
- Good management practice
Hazard ?
Any item, substance, activity or condition that has the potential to cause injury, damage or loss.
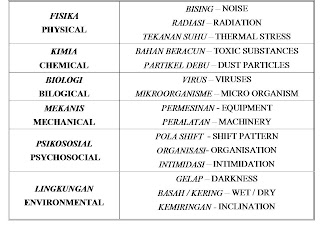
Types of hazards
Identifying the Hazards
- Walk around the workplace and look afresh at what could be reasonably expected to cause harm.
- Ignore the trivial and concentrate on significant hazards which could cause significant harm.
- Ask the workers what they think and what concerns them!
- Scrutinize the manufactures instructions and data sheets this will also assist you with the identification of hazards.
- Scrutinize the incident and health records.
- Scrutinize previous inspection and observation records.
- Evaluate every work site in terms of all the energy sources.
Risk
- Is the chance or probability that one or more hazards can meet and result in a loss of some description
- Is not about what will happen !
- It is more about what might happen
- As there is always a factor of uncertainty involved in risk
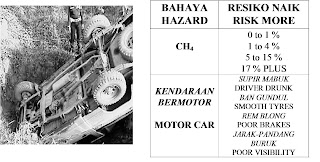
Determine Risk Potential
Risk Potential = Probability x Severity x Frequency
Calculate the Risks Arising from the Hazards
1. Probability
The chance of injury, damage or loss occurring
2. Frequency
How often can the hazardous event occur
3. Severity
The likely severity or outcome of the event
Concerns
The assignment of numbers or a score value, has no direct meaning or impact on improving safety.
Types of hira
- Job / task
- Continuous
- Process flow
- Issue based
Hira methods
- Fault tree analysis
- Hazard and operability study
- Failure mode and effect study
- Checklist
- Analysis / brainstorming
- What if ?
- Job safety analysis
- Management oversight & risk tree
- Event tree analysis
- Safety audits
Method choice
- Situation and type of operation
- Level of knowledge and expertise
- Complexity of operation
- Level of exposure to risk
- Number of persons involved